

New Zealand is perhaps one of the most exciting and influential wine regions in the world. It's location, topography and geologic origins provide the ingredients to make some of the most emblematic wines in the world.
Its history and contributions to the world of wine are realitively new yet, New Zealand's impact on the world's marketplace are nothing short of revolutionary.
New Zealand is 1,000 miles from Australia, the nearest landmass. The country is composed of two main islands (North Island and South Island) and runs north and south, much like California. New Zealand is about 990 miles long and about 180 miles wide on average.
Wine Regions of New Zealand The 1,000 miles of ocean between NZ (pronounced “En Zed” by the Kiwis) and Australia is the Tasman Sea. If moved to the equivalent latitude in the northern hemisphere, New Zealand would stretch from San Diego to Portland, OR. In perspective, New Zealand’s image as a wine region far outstrips its actual size. The total vineyard acreage of the country is roughly one third of the Napa Valley’s (and Napa is only 30 miles long).
The 1,000 miles of ocean between NZ (pronounced “En Zed” by the Kiwis) and Australia is the Tasman Sea. If moved to the equivalent latitude in the northern hemisphere, New Zealand would stretch from San Diego to Portland, OR. In perspective, New Zealand’s image as a wine region far outstrips its actual size. The total vineyard acreage of the country is roughly one third of the Napa Valley’s (and Napa is only 30 miles long).
The very northern tip of North Island is just about even with Adelaide, Australia, meaning that the wine regions of New Zealand are more southerly than those in Australia.
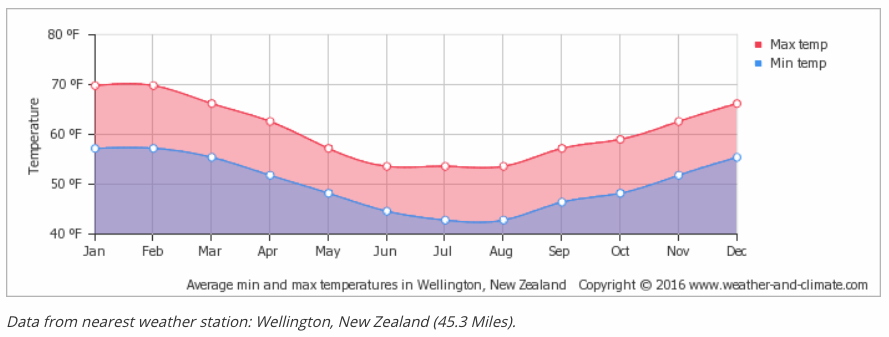
The climate of the country is maritime (affected by the sea) except for a small area on south-central South Island called Central Otago. All of the wine-growing areas are on the east coast of both islands to gain every ounce of heat in this cool, cool climate. This uses the west side of the landmass and mountains for shelter against the cold westerly winds. The saving grace is the high amount of direct sunshine available during the growing season. The average annual rainfall figures look a lot like our North Coast – about 35 inches that falls in the dormant season.
These factors drive the world class flavors in their emblematic Sauvignon Blancs, Alsatian style Pinot Gris, Champagne suggestive bubbly, Bordeaux like Cabernet Sauvignons,and Burgundian class Pinot Noirs.
Key Statistics
 Follow @gowinecom1
Follow @gowinecom1